About Council - VFS
The Financial Stability Council is the inter-institutional body that designs the macroprudential policy of the Republic of Croatia. It consists of representatives of the Croatian National Bank (HNB), the Croatian Financial Services Supervisory Agency (Hanfa), the Ministry of Finance (MF) of the Republic of Croatia and the Croatian Deposit Insurance Agency (CDIA).
Figure 1 Members of the Financial Stability Council
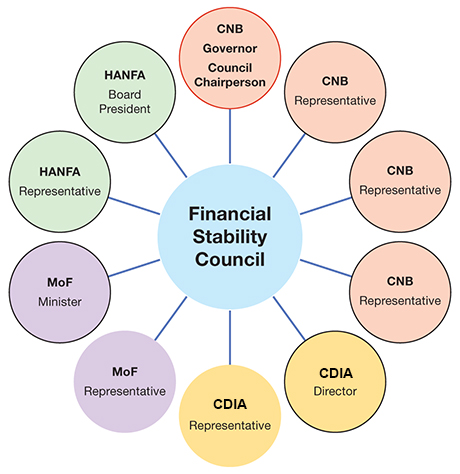
Note: The line around a circle denotes a voting right. In the event of a tie, the Council chairperson has the casting vote.
Financial Stability Council
The Financial Stability Council was established under the Act on the Financial Stability Council adopted by the Croatian Parliament in late 2013. The Act regulates the issues in the area of financial stability, the design and implementation of macroprudential policy and its objectives, the establishment, working methods and competence of the Council and other issues relevant for the design and implementation of macroprudential policy.
The Financial Stability Council is the inter-institutional body that designs the macroprudential policy of the Republic of Croatia. It consists of the following representatives of the CNB, HANFA, MoF and CDIA:
- Prof. dr. sc. Boris Vujčić, CNB Governor, Council chairperson,
- Dr. sc. Sandra Švaljek, Deputy Governor
- Dr. sc. Tomislav Ćorić, Vicegovernor
- Mr. sc. Vedran Šošić, Chief Economist
- Dr. sc. Marko Primorac, minister of finance
- Hrvoje Radovanić, Director of the Directorate for Public Debt Management, Ministry of Finance
- Dr. sc. Ante Žigman, President of the Board (Hanfa)
- Dr. sc. Tomislav Ridzak, Member of the Board of Hanfa
- Marija Hrebac, Chief Executive Officer (CDIA)
- Branka Križanić, Resolution Manager (CDIA)
Secretarial assistance to the Council is provided by the CNB. Meetings of the Council are held at least twice a year, and decisions are adopted by the majority of the votes of present Council members with a voting right.
Under the Act, the main tasks of the Council shall be:
- to design the macroprudential policy of the Republic of Croatia;
- to identify, assess and address systemic risks;
- to ensure cooperation and exchange of information between the competent authorities for the purpose of implementing the Act on the Financial Stability Council, in particular in crisis situations;
- to take actions related to the fulfilment of the requirements specified in ESRB warnings and recommendations and to prepare adequate explanations in case such requirements are not fulfilled;
- to align the methodology for identifying systematically important financial institutions or structures;
- to issue warnings and recommendations related to systemic risks and financial stability;
- to participate in the design and implementation of actions related to the recovery and resolution of credit institutions and non-banking financial institutions;
- to participate in the design of deposit insurance schemes;
- to participate in the design of investor protection schemes; and
- other tasks established under the Act on the Financial Stability Council.
The most important power of the Council concerns the issuance of warnings and recommendations to the competent authorities, other government administration bodies and legal persons with public authorities in the Republic of Croatia. The purpose of warnings is to draw attention to systemic risks that may threaten financial stability, while warnings indicate the need to introduce new or amend existing measures and instruments to be taken with the objective of safeguarding financial stability in the Republic of Croatia. The bodies and legal persons to which the Council issued a recommendation are obligated to act in accordance with that recommendation and to report regularly to the Council on the actions taken regarding the implementation of the recommendation.